Transmission Differences Between Viruses and Bacteria
While there are many similar symptoms, there are a lot of differences between viruses and bacteria. Many bacterial infections are contagious, which means we can pass them from person to person. According to the World Health Organization, there are many ways this can occur, such as close contact with a person who has a bacterial infection, touching them, or kissing them. We can also pass them along in an infected person’s bodily fluids, particularly after sexual contact or when an infected person coughs or sneezes. During pregnancy or delivery, mother-to-child transmission is another possibility, as is coming into contact with contaminated surfaces, such as doorknobs or key handles, and then touching your face, nose, or mouth. In addition to being spread between people, bacteria can also be transmitted through the bite of an infected insect. Consuming contaminated food or water can also lead to infections.
Like the previous infections, many viral infections are also contagious. Viruses can be transmitted between people in many of the same ways as bacteria. Coming into close contact with a person who has a viral infection or with the body fluids of someone with a viral infection, as in mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy or childbirth and coming into contact with contaminated surfaces. Also, like bacterial infections, viruses can be transmitted by an insect bite or by consuming food or water that is contaminated.
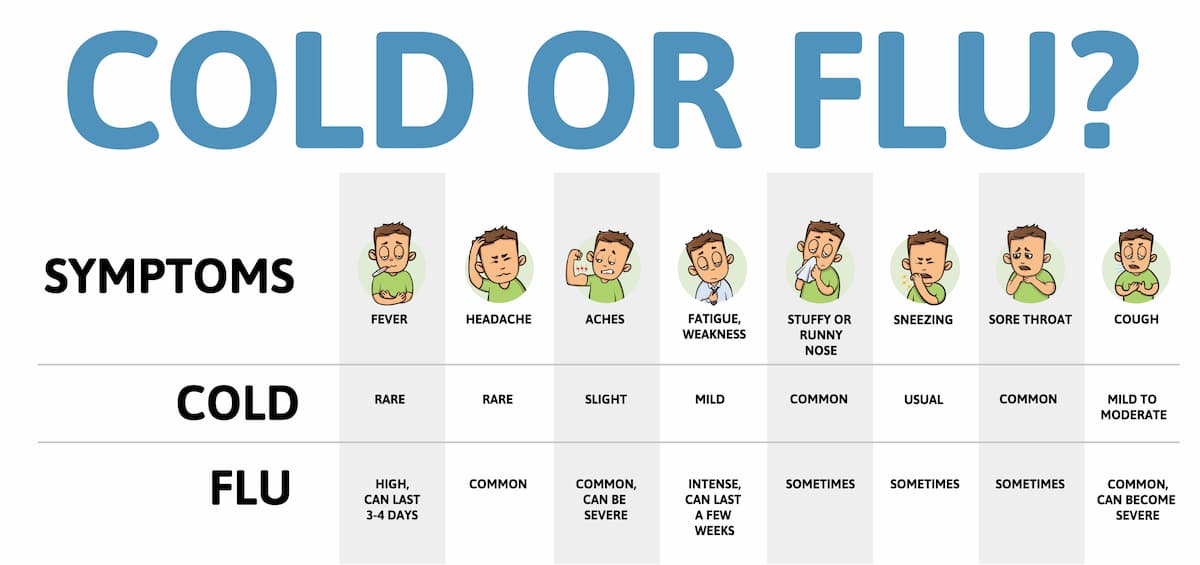
Cold

Diagnosis
Treatments

Antibiotics are drugs used to treat bacterial infections, and this is one of the main differences between viruses and bacteria. There are many different types, but they all work to prevent bacteria from growing and dividing effectively. Antibiotics are not effective against viral infections. Overprescribing can lead to resistance, which occurs when bacteria adapt and become able to resist certain antibiotics.
There is no specific treatment for many viral infections. Generally, treatment focuses on relieving symptoms, while the body works to clear the infection. Drinking fluids to prevent dehydration, getting plenty of rest, using pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to relieve aches, pains, and fever, or taking decongestants to help with a runny or stuffy nose are the best ways to deal with a virus.
Prevention
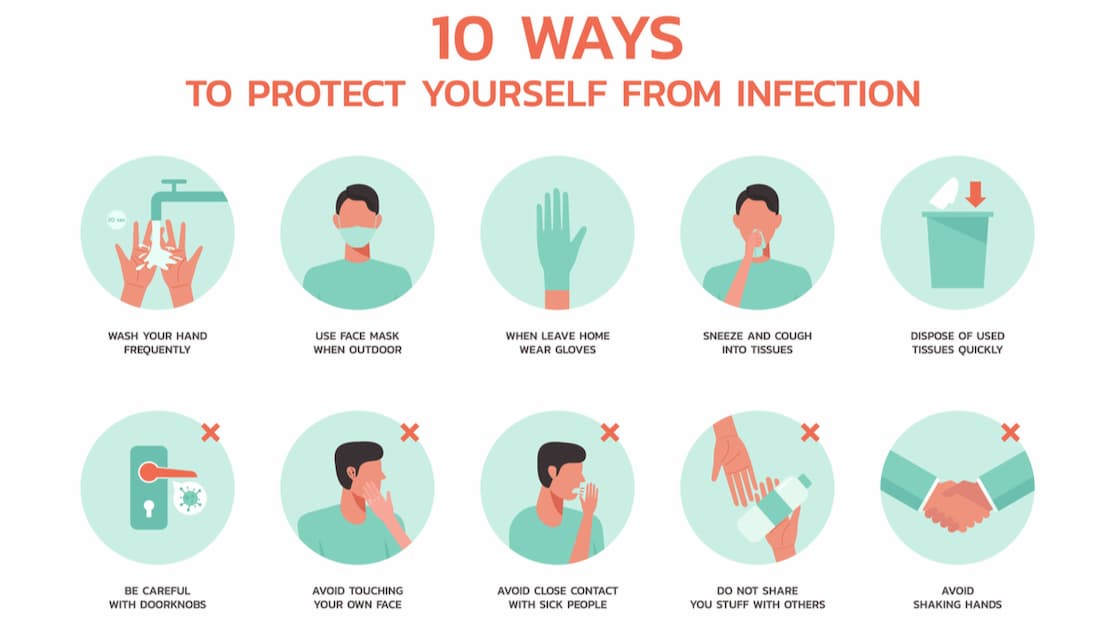
There are a significant number of differences between viruses and bacteria, but here are some of the tips that we should follow to help avoid getting sick with both a bacterial or viral infection.
- Get vaccinated: Many vaccines are available to help prevent various diseases of one kind or another. Examples of vaccine-preventable diseases are measles, flu, tetanus, or whooping cough.
- Well-cooked food: All meats must be cooked to the right temperature. Also, wash raw fruits or vegetables well before eating them. It is crucial not to allow leftover food to stay at room temperature; they should be refrigerated immediately.
- Do not go out if you are sick: Stay home if you have an illness of this type to help prevent the spread of infection. If you must go out, wash your hands frequently and sneeze or cough into the crook of your elbow or a tissue. Make sure to dispose of used tissues properly.
- Practice good hygiene: Be sure to wash your hands before eating, after using the bathroom, and before and after handling food. Avoid touching your face, mouth, or nose if your hands are not clean. Do not share personal items such as eating utensils, glasses, towels, or toothbrushes.

